Hereditary pattern baldness affects many men and women. It is identified by both the pattern of hair loss. Your family history of hair shedding of a similar type will also tell whether it is hereditary. However, genetic hair loss is often the result of hormonal disturbance, genetic predisposition, and natural aging.
What percentage of hair loss is genetic?
Research finds that 80 percent of people with baldness have a history of hair loss. In many cases, the father also lost hair. However, baldness genes may not affect all generations. In fact, they are random in terms of siblings they will affect. Some siblings may receive genetic baldness from their genes, while others may still remain immune to it. Genetic hair loss is known as androgenetic alopecia or male/female pattern baldness.
Male pattern baldness starts at the hairline. As a result, men start getting bald on the forehead and at the temples. This extends backward, causing baldness along the scalp sides and top. It may start in the late teens or early 20s. Pattern baldness in women rarely causes complete baldness. A woman may experience hair thinning on the top and along the sides of the head. Genetic hair loss in men and women is different, as men exhibit receding hairlines more than women.
Is hair loss inherited from mother or father?
Many people believe that men inherit hair loss from their mother’s side while women get it from their father’s side. The reality is that no one family side has a role in hair loss. In fact, hair loss genes are passed down from both sides.
Can we stop genetic hair loss?
Hereditary hair loss cannot be prevented, as your genes are involved in it. Hair loss is a 4-step cycle, from growth to the resting stage. Then there is the third stage, when hair falls out, which is followed by regeneration.
Genetics alone is not responsible for hair loss. Other factors contribute to the problem. Hormonal disturbance in women is a major cause of hair loss. Many women experience baldness during menopause. On the other hand, men start getting bald in early adulthood.
An autoimmune condition may also be responsible for hair loss. Such type of hair shedding is known as alopecia areata, which results in patchy hair loss.
Some people may suffer hair shedding apart from genetic hair loss due to a medical condition, such as traumatic alopecia or ringworm infection.
Tight hairstyles may also play spoilsport in hair growth. You may suffer hair loss if you tie your hair tightly. This type of hair loss is known as traction alopecia.
Certain medical conditions also put you at a high risk of hair loss. This includes all metabolic diseases, including thyroid, diabetes, and IBS. Additionally, chemotherapy-induced hair shedding is no secret.
Genetic hair loss treatment
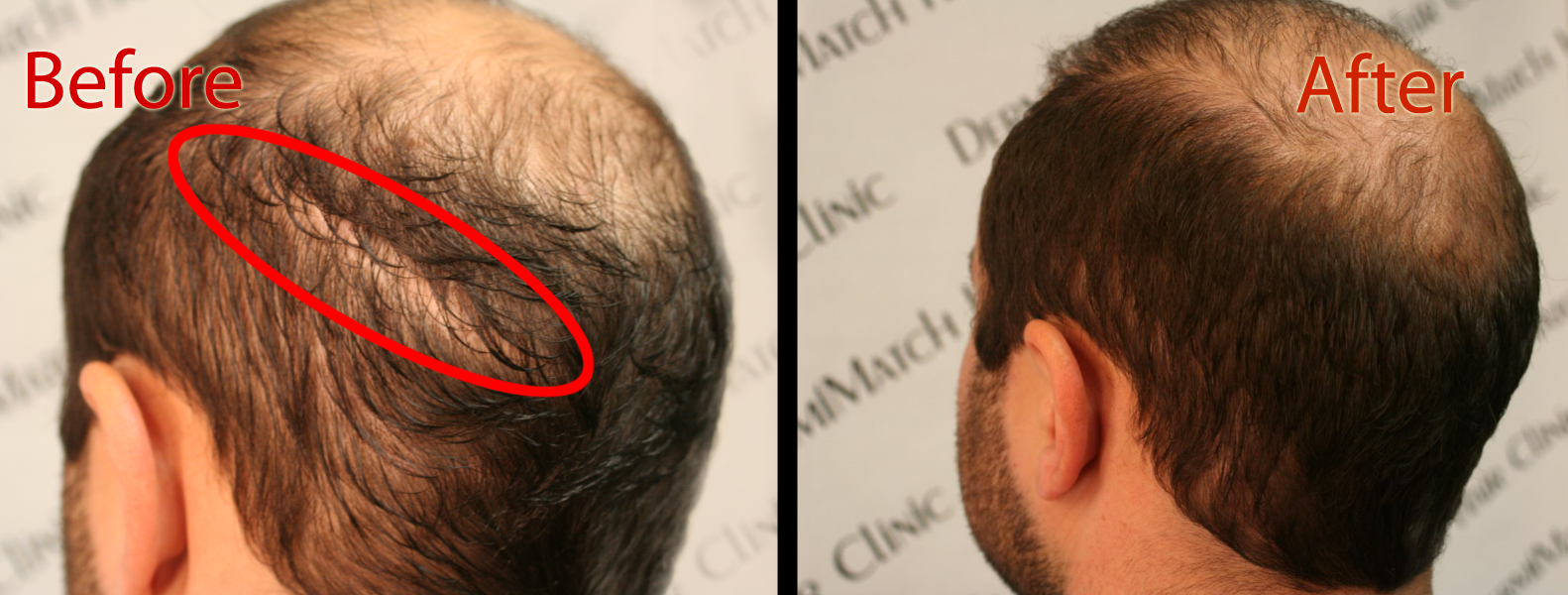
Struggling with hair loss and looking for a solution? Well, scalp micropigmentation is a permanent solution to hair shedding. If yours is genetic hair loss, there are hardly any solutions to the problem. Here, SMP can come to your rescue and conceal the problem areas.
Get help from the top Arizona SMP practitioners at DermiMatch Clinic – your one-stop shop for all things scalp micropigmentation and hair loss.