Hair loss is a widespread concern that affects millions of individuals, often linked to genetic factors. Androgenetic alopecia, also known as pattern baldness, is a form of genetic hair loss. Does that mean your genes are blamed for this hereditary condition?
Well, the condition is believed to be caused by genetic factors and impacts both men and women, although the patterns of hair loss can differ significantly between genders. So if someone asks whether there is a connection between genetics and hair loss, the answer is yes.
Understanding Genetics and Hair Loss Connection
Hormonal disturbance is often blamed for genetic hair loss. Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) is a derivative of testosterone and plays a significant role in the hair growth cycle. An elevation in DHT levels can affect the hair growth cycle and cause hair follicle shrinking, resulting in thinner and weaker strands of hair. You should not be surprised if this process results in noticeable hair loss.
The patterns of hair loss vary significantly between men and women.
Male Pattern Baldness
This condition is characterized by a receding hairline, often beginning at the temples and progressing to thinning at the crown of the head. Men may notice that their hair becomes sparse in these areas, leading to a more pronounced baldness over time.
Female Pattern Baldness
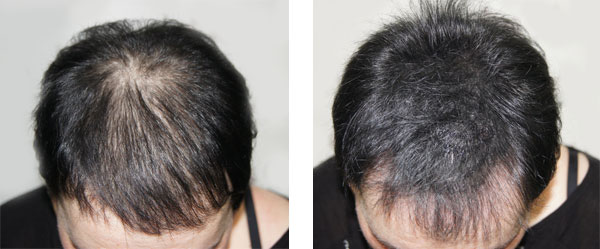
In women, hair loss usually presents as a diffuse thinning of hair across the scalp, particularly noticeable along the parting line. Unlike men, women generally do not experience a receding hairline, but the overall volume of hair may decrease, which can be equally distressing.
Can You Manage Genetics and Hair Loss?
Well, you can’t control your genetics, but you can do something about genetic hair loss. Yes, it is possible to improve your appearance despite hereditary hair loss.
Medications
Minoxidil is a topical solution used to stimulate hair growth. It is available over the counter and is applied directly to the scalp. Consistent use may help hair growth but it stops as soon as the topical application is discontinued.
Finasteride is a prescription medication that works by reducing DHT levels in the body. It is primarily used for men and has been shown to slow hair loss and promote regrowth in some cases.
Hair Transplant
This surgical procedure involves relocating hair follicles from a donor area, often the back of the head, to the balding regions. Hair transplants may not be complete in one session and may require multiple sessions and come with associated costs and recovery time. Besides, there could be side effects and pain from a transplant.
Gentle Hair Care
It’s important to avoid harsh hair products, excessive heat styling, and tight hairstyles that can pull on the hair and contribute to breakage. Opting for mild shampoos and conditioners can help maintain scalp health. But that doesn’t solve the problem of genetic hair loss.
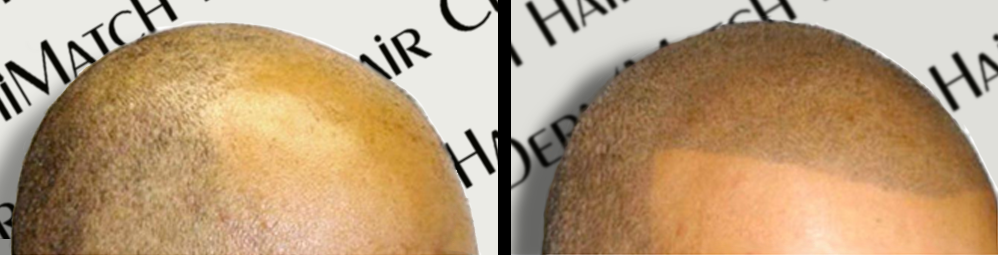
Is SMP A Solution to Genetic Hair Loss?
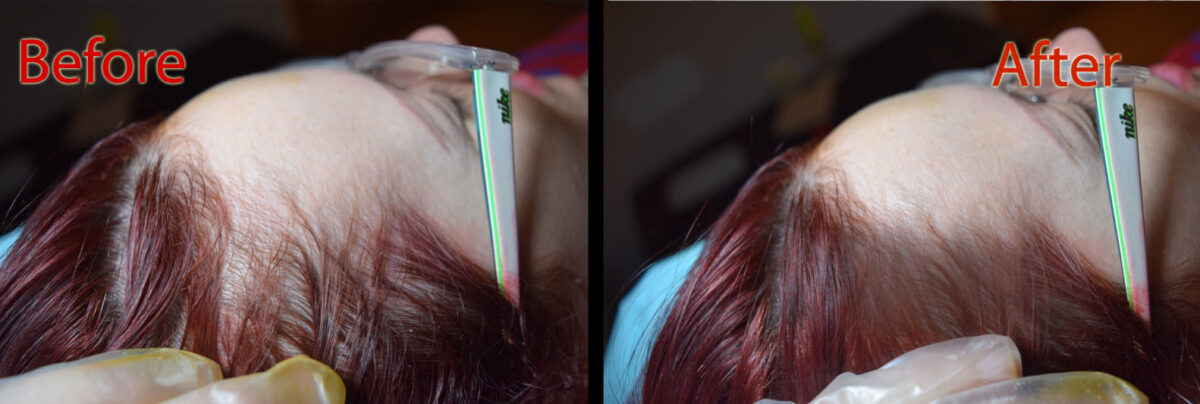
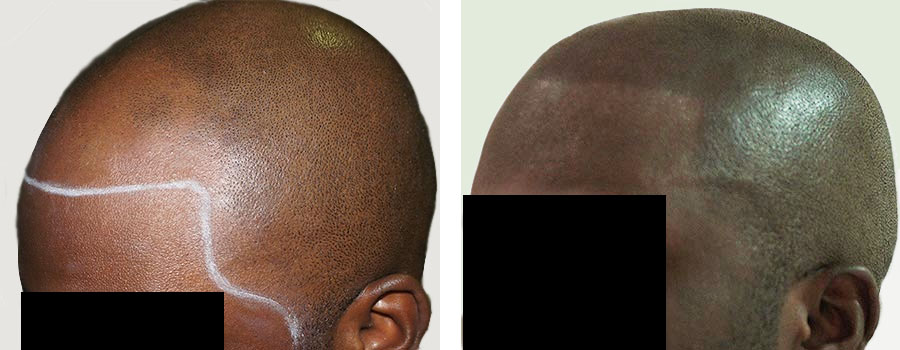
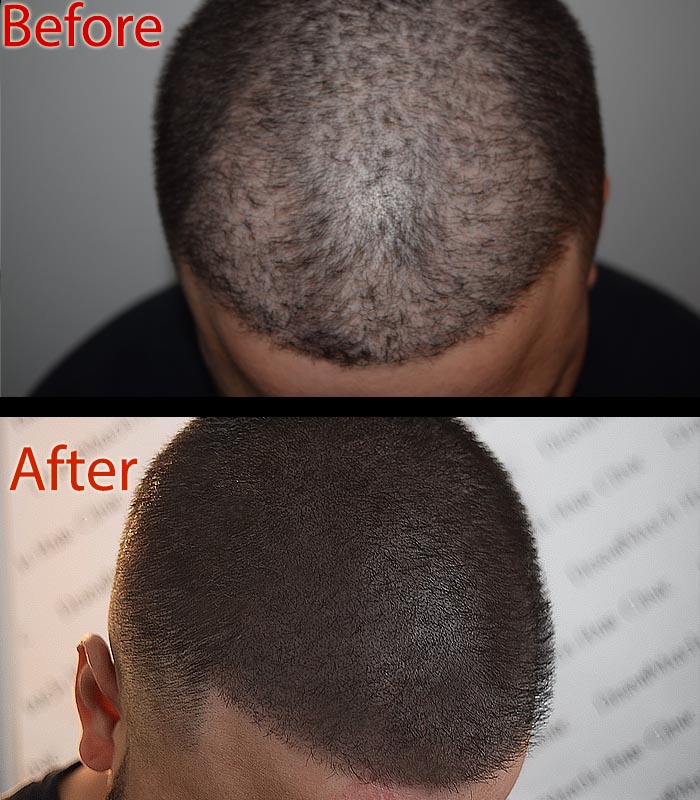
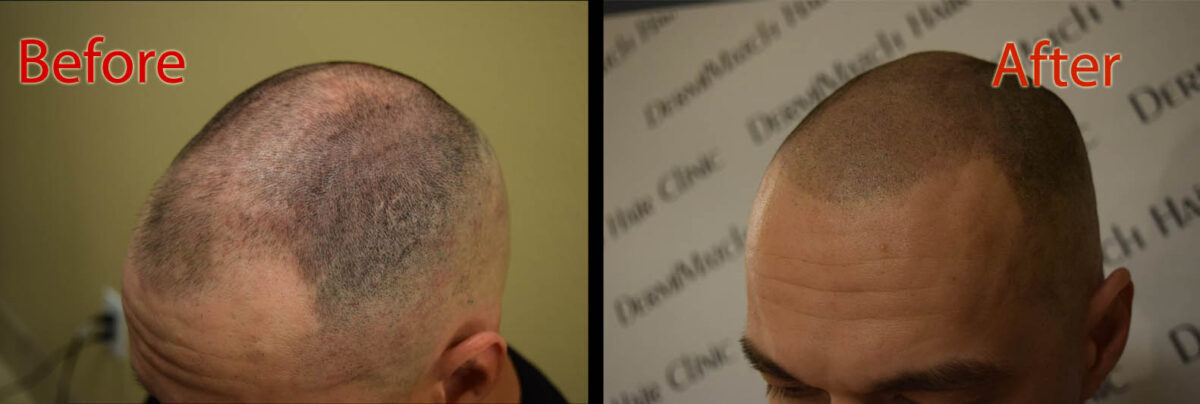
For those dealing with significant hair loss, scalp micropigmentation offers a non-surgical solution. This innovative technique involves tattooing tiny dots of pigment onto the scalp to mimic the appearance of follicles. It can effectively camouflage hair loss and restore confidence, providing a fuller look without the need for surgery.
The best thing about the procedure is that it can hide any signs of scalp problems, even if there is a connection between your genetics and hair loss.
It can help regain a sense of control over your appearance and well-being. Get help from Arizona SMP professionals. Top scalp micropigmentation experts are available at DermiMatch Clinic. They have been in the field of scalp micropigmentation since its beginning and proud to have a successful stream of happy clients.